In an era marked by rapid technological advancement and climate change, digital technology companies stand at the forefront of the global transition to a net-zero society. The environmental impact of the digital industry is complex, presenting both benefits and challenges. Its potential to drive climate change monitoring, energy optimization, and the adoption of low-emission technologies becomes evident; yet digitalization also sparks environmental concerns, including about increased energy consumption and greenhouse (GHG) emissions.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the UN agency for digital technologies, is tasked with assessing the impact of its industry, and is developing a database to monitor digital industry emissions and climate commitments. In its 2024–2027 strategic plan, Target 2.5 focuses on boosting the role of ICT in climate and environmental action, measured by indicators such as the contribution of telecommunications/ICTs to global GHG emissions. A key step is the development of a robust emissions database, which will track digital industry emissions and climate commitments.
The Greening Digital Dashboard serves as a gateway to track how the ICT sector can contribute to climate goals.
Driving a Green Digital Future
Learn more about ITU’s efforts to drive a sustainable, green digital future for the ICT sector.
Partnership for change
In 2023, ITU and the Green Digital Action partners launched an initiative to reduce GHG emissions across the ICT sector, emphasizing enhanced monitoring, transparent reporting, and effective reduction strategies.
In addition, ITU and the World Benchmarking Alliance have been collaborating on the ‘Greening Digital Companies: Monitoring Emissions and Climate Commitments’ report, now in its third edition. These reports offer a comprehensive assessment of GHG emissions and energy consumption across 200 digital companies – a key resource for this dashboard, which includes data from the 2024, 2023 and 2022 reports.
Why we must act
Digital companies play a crucial role in the global shift to a low-carbon economy. The ICT sector accounts for 1.5%–4% of global GHG emissions, comparable to aviation.
To align with the Paris Agreement and cap warming at 1.5°C, the sector must cut emissions by 45% by 2030. This requires science-based targets, transparent reporting, and clear transition plans.
Industry commitments for green digital transformation
The Green Digital Action initiative calls on ICT companies to take two primary actions:
- Set 1.5°C aligned science-based targets, to be validated by SBTi, for emissions reduction, and commit to reduce accordingly scope 1, 2 and 3 emissions, as well as create and publish transition plans outlining how decarbonization trajectories and net-zero targets will be achieved.
- Report data on all GHG emission scopes and categories yearly and publicly, and submit results to a public ITU database.
Tracking progress using the Greening Digital Dashboard
The Greening Digital Dashboard enables ITU and partners to track the ICT sector’s climate impact and set science-backed targets.
It lays the groundwork for an ITU-led ICT GHG emissions database, supporting global climate goals.
ITU data highlights:
An increase in energy consumption and GHG emissions, fueled by growth in artificial intelligence and data centres.
ITU data highlights:
The lack of data to fully track the sector’s environmental impact.
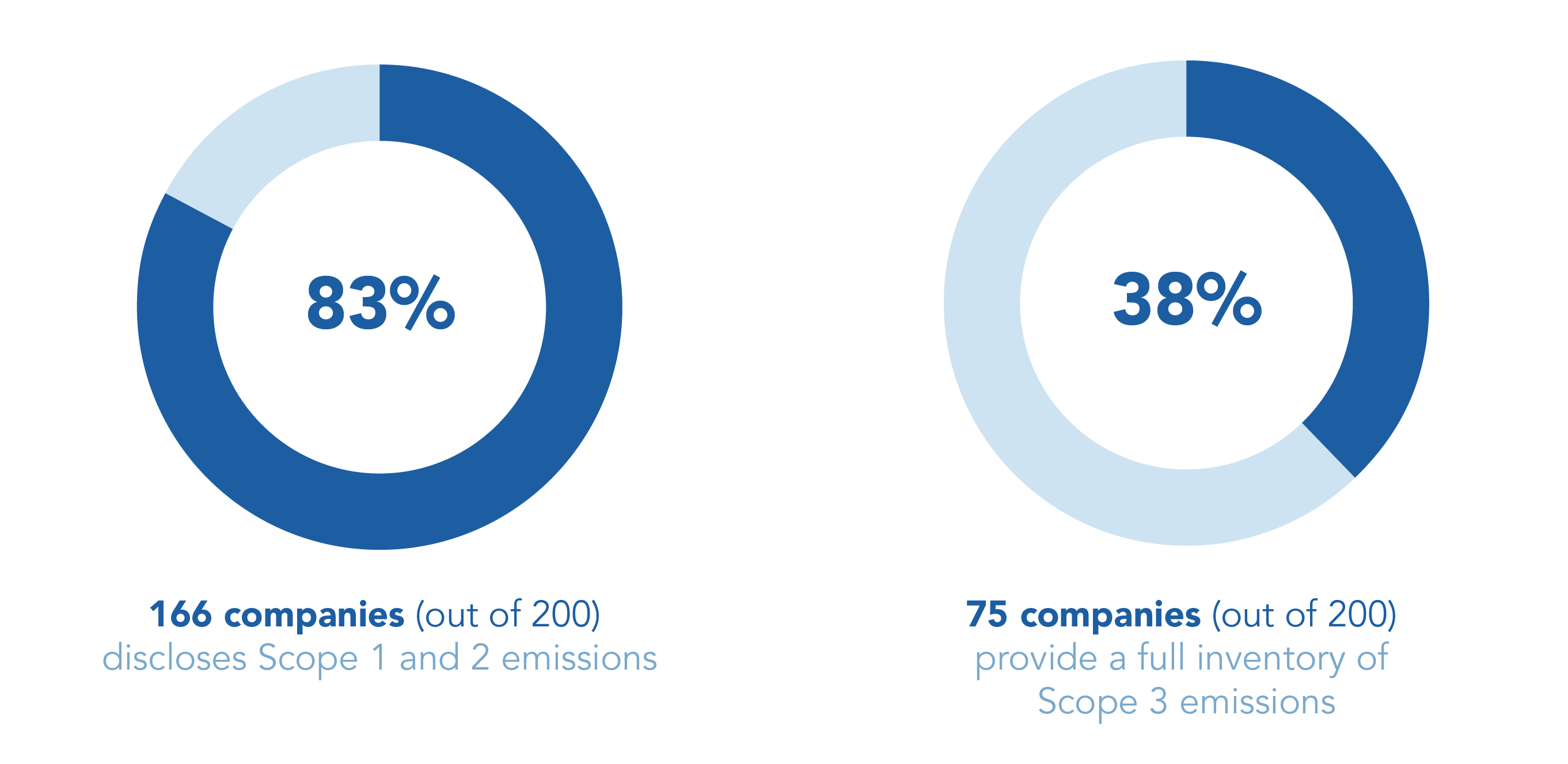
Proportion of companies reporting:
Companies and governments must track the digital sector’s environmental footprint, and at a minimum report the following indicators:

✔ Scope 1 GHG emissions
✔ Scope 2 Location-based GHG emissions
✔ Scope 2 Market-based GHG emissions
✔ Scope 3 GHG emissions by all relevant GHG Protocol categories

✔ Total energy consumption
✔ Total electricity consumption
✔ Renewable electricity used

✔ Third-party verification of Scopes 1, 2, and 3 GHG emissions data
✔ Companies with a dedicated climate report
Recognizing the need for climate action, ITU calls on digital companies and ICT regulators to monitor the ICT sector’s environmental impact. ITU is supporting countries through a newly launched working group on environmental indicators, under the ITU-D Expert Group on Telecommunication/ICT Indicators (EGTI).
Strengthening national capacity for gathering and reporting environmental data, will help to build a harmonized, data-driven approach to reducing emissions, managing energy resources, and minimizing environmental impacts.
Increasing transparency and access to environmental data of the ICT sector is central to building a green digital future.
For more details, contact: eetmail@itu.int
Learn more about the Green Digital Action GHG pillar.